Is there really any way to heal hearing loss, ringing and vertigo naturally? New studies show that certain nutrients can repair hearing loss and ringing in the ears, and simple “maneuvers” can help vertigo. Hearing is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations and changing pressure through the ear. Some people may have noise induced hearing damage while others may lose hearing as they age. There are four stages to hearing loss: mild, moderate, severe and profound. Hearing can be measured by behavioral tests using an audiometer at your doctor’s office.
According to the following research, the right nutrients can restore damaged hair cells, repair noise-induced hearing loss, increase circulation to our ears, improve auditory nerve function, and even silence ringing and buzzing in the ears:
HEARING LOSS
A group of government scientists conducted a 6-month study on the benefits of a natural remedy for hearing loss. And they tested it on 1,000 marines at Camp Pendleton who were undergoing rifle training. At the beginning of the study, the scientists gave 600 marines an amino acid called N-acetyl cysteine. The other 400 were given a placebo. The marines took hearing tests before and after the rifle training. 70% of the marines taking N-acetyl had less hearing loss. N-acetyl cysteine helps repair the ear damage caused by loud noises and boosts the body’s production of an antioxidant called glutathione. Studies show that people with hearing problems tend to have low glutathione, and N-acetyl boosts glutathione levels. Alpha Lipoic Acid, an antioxidant and Acetyl-L-Carnitine, an amino acid also help to improve your range of hearing and repair damaged hearing.
In another hearing study, scientists gave these same two nutrients to aging rats for six weeks. The researchers divided the subjects into three groups. Group 1 received Alpha Lipoic Acid. Group 2 received Acetyl-l-Carnitine. Meanwhile, the control group, Group 3, didn’t receive any supplements. At the end of the study, the rats that didn’t take any supplements saw a normal deterioration of their hearing. The rats taking the Alpha Lipoic Acid or Acetyl-l-Carnitine avoided hearing loss and their hearing actually improved. Scientists discovered that Alpha Lipoic Acid was more effective for protecting hearing at low frequencies, and Acetyl-l-Carnitine worked better for higher frequencies.
RINGING IN THE EARS
In another study with 103 patients who suffered with ringing in the ears. participants were given Ginkgo Biloba or a placebo. At the end of 13 months, every single person in the ginkgo group reported an improvement in their hearing. Ginkgo is a natural vasodilator that widens blood vessels and it also has flavones and ginkgolides which are antioxidants that help protect inner ear hair cells and the auditory canals.
VERTIGO
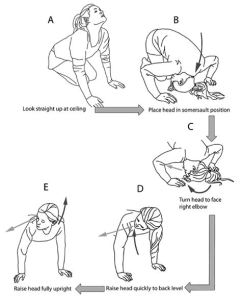
It is very difficult to function with vertigo if you have ever had it. There is a study on vertigo entitled, A Comparison of Two Home Exercises for Benign Positional Vertigo: Half Somersault versus Epley Maneuver. In this study, Dr. Carol Foster of the University of Colorado School of Medicine tested a new do-it-yourself exercise, called the “Half Somersault Maneuver” to treat the most common form of vertigo. Dr. Foster, who is director of the Balance Laboratory at the CU School of Medicine treated herself with this maneuver and says that this exercise causes the “particles to leave the semicircular canal.” She said the she was completely surprised at how well this works on most patients.
Here are Dr. Foster’s steps to help counteract vertigo:
- Patients put their head upside down like they are going to do a somersault.
- They wait for dizziness to end then raise their head to back level.
- They then wait again for dizziness to end and then sit back quickly.
Music, loud noises, age, infections, diseases and even some medications can all contribute to hearing loss, so it is always important to take good care of your ears while you can.
Other Research Studies:
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10733178
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11583389
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2947100
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8135325


Leave a Reply